Ref - Link
Different Loss Types
U-Net and its variants for medical image segmentation: theory and applications
Basic Unet
Attention U-net
- An often-desirable trait in an image processing network is the ability to focus on specific objects that are of importance while ignoring unnecessary areas. The attention U-net achieves this by making use of the attention gate
- Repeated uses of the attention gate after each layer improves segmentation performance significantly without adding too much computational complexity to the model.
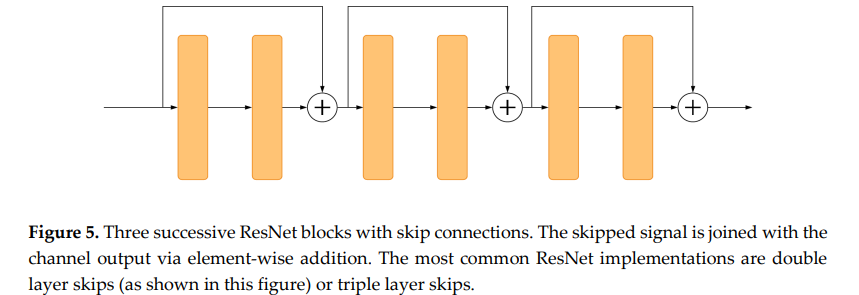
Residual U-Net
- ResNet uses skip connections which take the feature map from one layer and add it to another layer deeper in the network.
Dense U-net
Dense U-nets employ DenseNet [67] blocks in place of regular layers. While the ResNet model
allows for deeper neural networks, it does not eliminate the problem of vanishing gradients. ResNet architecture also eventually degrade in performance with increasing layers.
U-net++ is another powerful form of the U-net architecture inspired from DenseNet [67]. It uses a dense network of skip connections as an intermediary grid between the contracting and expansive paths
An adversarial model is a setup where two networks compete against each other in order to
improve their performance. Generative adversarial networks (GAN) are a novel type of adversarial process used to generate new data
- Perceptual loss function [3] during training. map the predicted SR image I and the target image IHR into a feature space and then measure the distance between the two mapped images in the feature space
Keep Exploring!!!
















No comments:
Post a Comment